The most obvious and visible signs of aging are changes in the appearance of the skin. The skin serves as the first line of defense against pathogens and is the largest organ chronically exposed to the environment and displayed to others [1]. Its appearance reflects overall health and communicates ethnic identity, lifestyle, and age. These characteristics are largely determined by skin color, texture, firmness and smoothness, which are also significantly affected by the aging process. Over time, skin typically becomes unevenly pigmented, rough, loose and wrinkled [2].
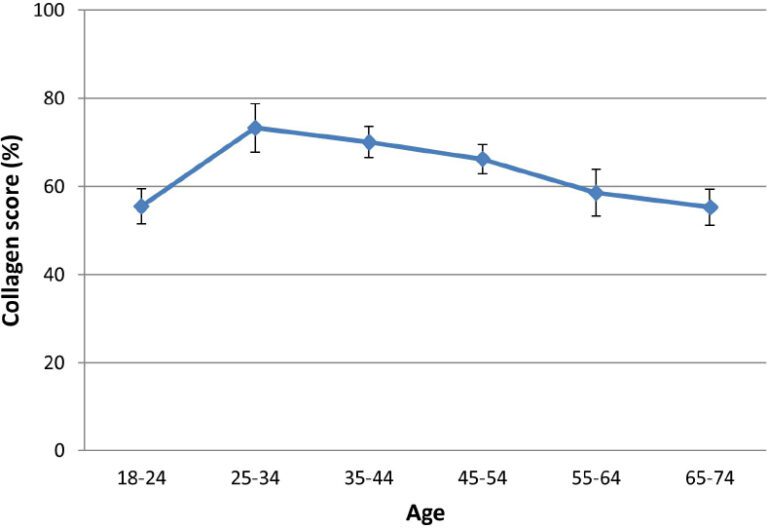
Beginning in early adulthood, fibroblasts become less active and collagen production decreases by approximately 1.0% to 1.5% per year [3]. Although collagen deficiency can begin as early as the twenties, it is a gradual process that may not become noticeable until later in life. In most cases, it becomes apparent between the ages of 40 and 60, when adaptation to change becomes somewhat compromised, and this period is associated with the development of age-related diseases [1].
Impact of Sunlight on Collagen Depletion
Despite the ongoing process of regeneration, the skin’s ability to regenerate diminishes due to constant exposure to external irritants such as air pollution and diet, and changes in its appearance directly signal ongoing pathological changes in the body. Damage caused by exposure to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) radiation further accelerates the process, as sun-exposed areas of the skin, typically the face, neck, upper chest and hands, tend to undergo more rapid changes compared to sun-protected areas. Slightly more pronounced changes occur in people with fair skin, as higher pigmentation provides some protection against the harmful effects of UV radiation [2].
Why Do We Need Collagen in the Body?
Collagen is an essential protein structure that gives skin its smoothness and elasticity. Its production decreases with age, leading to collagen deficiency. Natural aging processes and various diseases lead to changes in the composition, structure and mechanical strength of connective tissue, which is rich in collagen proteins [4]. Collagen is critical for maintaining the strength and elasticity of tissues, and age-related changes manifest as skin wrinkling, bone and cartilage deterioration, and cardiovascular and respiratory problems [5].
Clinical evidence over the past decades has shown that both external and internal factors can negatively influence collagen metabolism and degradation, promoting its degradation and inhibiting its formation. An increasing number of scientific studies provide promising evidence that age-related skin changes or damage can be reversed, joint function can be improved, and personal well-being and vitality can be supported [3].
Factors Affecting Collagen Deficiency
Important factors influencing collagen production include life stages such as puberty, pregnancy and menopause, as well as internal and external factors such as genetic makeup, age, UV radiation, air pollution, smoking, alcohol consumption and others. With the development of new technologies, ingredients and devices for the renewal of collagen and matrix components, a growing number of strategies are beginning to target the components of the aging process and mitigate collagen deficiency.